
#MEDIAL MALLEOLUS AVULSION FRACTURE HOW TO#
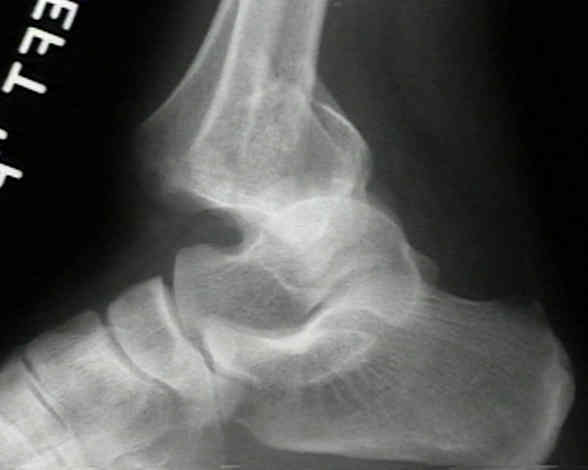
How to Differentiate Carotid Obstructions.TI-RADS - Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System.Head Neck tumors - When to think of malignancy.A majority of ankle fractures are the result of rotational forces. The break may occur by itself but it normally accompanies injuries to the outside of the ankle or a fibula fracture of the smaller of the two lower leg bones. Esophagus II: Strictures, Acute syndromes, Neoplasms and Vascular impressions Medial malleolar fractures involve the articular surface of the ankle joint, which is where the bones meet in the joint.Esophagus I: anatomy, rings, inflammation.Vascular Anomalies of Aorta, Pulmonary and Systemic vessels.Contrast-enhanced MRA of peripheral vessels.Ischemic and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy.Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System 2.0 Aetiology Commonly associated with rotational injuries of the ankle, this can occur either as an inversion or eversion injury.Bi-RADS for Mammography and Ultrasound 2013.Transvaginal Ultrasound for Non-Gynaecological Conditions.Acute Abdomen in Gynaecology - Ultrasound.Appendicitis - Pitfalls in US and CT diagnosis.
#MEDIAL MALLEOLUS AVULSION FRACTURE FULL#
Arthroscopic resection of the ossicle at the medial malleolus requires no additional treatments of the deltoid ligament, effectively relieves symptoms, and enables the patient to return to full preinjury activities.ģ-dimensional computed tomography ankle deltoid ligament secondary ossification center surgery.Ĭopyright © 2015 American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons. The patient fully recovered and was able to return to sports activities 3 months after surgery. The deltoid ligament sustained minimal damage after resection. The ossicle was resected in a step-by-step manner with an arthroscopic shaver and grasper through the anteromedial accessary portal. Instability of the ossicle was identified after the hypertrophic inflammatory synovium had been debrided. Conservative treatment failed, and the patient underwent ankle arthroscopy. injury patterns: - deep deltoid ligament may be torn, leaving malleolus intact - anterior colliculus may be avulsed by superficial deltoid, leaving deep. Plain radiography and computed tomography revealed a small ossicle associated with the anterior colliculus of the medial malleolus. We describe a patient with a symptomatic ossicle of the medial malleolus in the left ankle that prevented participation in sports activities because of medial ankle pain. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate or unnecessary treatments. An ossicle around the medial malleolus is difficult to differentiate from an unfused ossification center, an avulsion fracture, and os subtibiale.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
